
According to a scientific paper published in the European Journal of Human Genetics, approx. 300 million people (around 3.5-5.9%) are living with rare diseases, out of which 72% are genetic, and of those 70% start in childhood. A greater understanding of biology with the rapid adoption of revolutionary diagnostic and therapeutic technologies has unlocked treatment options for people with rare diseases. Many biotech and pharmaceutical companies are working towards the development of medicines that work to treat and manage diseases, considered as “undruggable” target. The precision medicines are curated identifying the factors that predispose an individual to a specific disease utilizing relevant data about the patient’s genetic makeup, behavioral patterns, and current lifestyle. Generally, an omicsapproach is followed to generate biological insights, and then the massive amount of the retrieved data set is analyzed, interpreted, and integrated leveraging Artificial Intelligence tools and algorithms to create customized drugs.
As AI enters the world of precision medicine, the technology can help pharmaceutical manufacturers to deepen their knowledge about the origins and course of many diseases. The global artificial intelligence in the healthcare market is anticipated to reach USD45.2 billion by 2026. More than 60 biotech companies are working towards advancing therapies for rare cancer conditions using advanced analytics capabilities.
AI technologies in medicine exist in multiple forms, from purely virtual to cyber-physical, which recognize sophisticated patterns that enable image-based detection. AI-enabled diagnostic intervention reduces the chances of errors while augmenting intelligence to support decision making, bias-free reasoning, prediction, efficient search, and address untraceable problems. The convergence of high-throughput genotyping and global adoption of electronic health records (EHRs) provides scientists with valuable data sets that help them derive new phenotypes and solve the most complex problems in personalized care.
One of the world’s largest biopharmaceutical companies, Pfizer collaborated with Concerto HealthAI to advance work in precision oncology utilizing artificial intelligence and real-world data. The partnership aims to develop and use medicines to improve patient outcomes for those who suffer from solid tumors and hematologic malignancies. Leveraging AI, Pfizer intends to identify new and more precise treatment options and accelerate the completion time of the research studies.
Another pharmaceutical giant, Janssen Pharmaceuticals (part of Johnson & Johnson) has joined hands with a French start-up to develop an AI-powered drug design system, in silico system, based on deep generative models. The AI tools could result in the fast identification of molecules with efficiency to meet the desired criteria of research projects.
Athos Therapeutics has also announced a research collaboration with Cleveland Clinic for the development of first-in-class precision therapeutics for patients suffering from inflammatory bowel diseases, resulting from the dysregulation of the immune system. Currently, prescribed drugs show limited efficacy and some potential side effects. However, the precision or custom-made therapeutics could help to characterize the heterogeneity of IBD at the molecular level and deliver long-lasting and safe therapeutic options.
Unlike traditional medicines developed using trial-based methods, precision medicine is curated utilizing correct findings, sensitive to some situations. The doctor suggests precision medicine based upon an individual’s DNA and personal health information therefore, corresponding analysis is important for determining the reliability and validity of the drug. As the name suggests, precision medicine is for precise treatment as the choice of the right drugs can largely reduce side effects and ensure great success.
Artificial intelligence models and methods are crucial for identifying casual genes from those with ‘variations of uncertain importance’, which was earlier difficult to determine with bioinformatics prediction. Besides, AI-based solutions such as Human Splicing Code and DeepSEA have shown incredible results for improving genetic diagnostics in neurodevelopment disorders and make correct classification of missense variants.
AI-based Health Assistants Changing the Future of Medicines
Many studies demonstrate the devastating rate of misdiagnoses ranging from 10%-40%, which is responsible for around 10% of patient deaths. Besides costing human lives, misdiagnoses account for losses worth USD750 billion in the USA and USD611.5 billion inEurope. Accurate diagnosis with advanced tools can save up to 30% of the total healthcare budget globally.
European Union-funded, Symptoma digital assistant has been designed to enhance diagnostic quality while reducing costs. The electronic health tool consists of a chatbot that uses artificial intelligence to ask questions from the user after he/she enters relevant information about his/her symptoms. With a database of around 20,000 diseases and billions of connections to symptoms and risks and factors, Symptoma quickly identifies symptoms specific to a certain disease. Unlike other symptom checkers, the online platform includes information on rare diseases. Thus, autonomous virtual assistants could deliver precision preventive medicine and reduce the severity of symptoms.
AI-based Applications in Precision Medicines
- Genome-Informed Prescribing
Genome-informed prescribing for patients with pharmacogenomically actionable variants is one of the many areas to demonstrate the power of precision medicine. The machine-learning algorithms are able to predict which patients are likely to need medication for which genetic information, which helps physicians suggest personalized dosages by genotyping the patient with AI-based solutions. AI techniques have proven to be beneficial for efficient genome interpretation and scientists have used the knowledge to identify links among genomic variation, disease prevention, therapeutic success, and prognosis. Radiogenomics, a novel precision medicine research field focuses on mapping co-relation between cancer imaging features and gene expressions that help clinicians develop the right treatment plan. Precision immuno-profiling by image analysis and artificial intelligence can help in assessing immuno-oncology biomarkers as a predictor of patient response.
- Deep Phenotyping
Several studies have demonstrated the utility of correlating phenotypes to feature of genetics that consequently results in decision making in precision contexts. Deep phenotyping means a precise and comprehensive analysis of phenotypic abnormalities aimed towards better diagnosis, patient stratification, and selection of best treatment strategies. A better understanding of the underlying molecular factors can contribute to molecular data profiling for providing the best available care to every individual. Hence, deep phenotyping can accelerate the identification of disease subtypes to develop better treatment strategies at a cellular level.
- Disease Subtyping
AI methods have pioneered the development of clinically relevant disease subtypes, which can be used for patient stratification. For instance, cancer is a heterogeneous category of disease and its tumor subtypes can be largely characterized by their tissue of origin based on the clinical information. Colorectal cancer research excelled gene expression subtyping efforts based on random forest classification leveraging machine learning technology. While tumor subtyping solely explores a single data modality, machine learning techniques jointly model data from various sources for multi-omics integration. Thus, deep learning empowers precision medicine by presenting meaningful information in cell cultures on the basis of molecular data.
Drug Combination
Monotherapies can often suffer from a low potency and lead to drug resistance, a common obstacle in oncology. However, drug combinations target-independent gateways or disease mechanisms to overcome resistance. The perfect cocktail of drugs requires computational methods that prioritize the most potent combinations without resulting in toxicity. Conventionally, drug signatures were utilized to obtain drug functional networks in which combinations were made by searching drugs whose target was enriched in a complementary disease-specific network.
Conclusion
Despite multiple advancements in treatment strategies, drug development remains an inefficient process. Without leveraging artificial intelligence methods, precision medicine is hard to realize in clinical practice. The convergence of AI and precision medicine is creating a future where health-related tasks are becoming highly personalized.
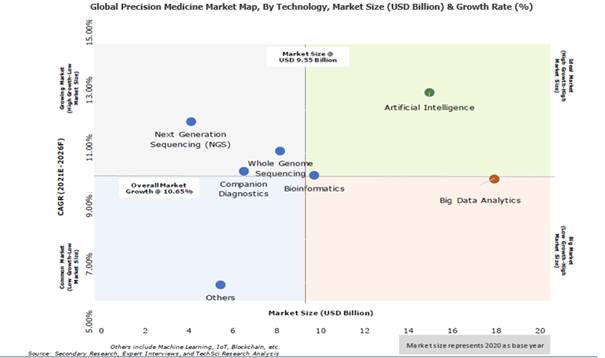
According to TechSci research report, “Global Precision Medicine Market By Products & Services (Precision Medicine Platforms, Precision Medicine Tools, Precision Medicine Services), By Technology (Big Data Analytics, Artificial Intelligence, Bioinformatics, Whole Genome Sequencing, Companion Diagnostics, NGS, Others), By Application (Oncology, Cardiology, Respiratory, Neurology, Immunology, Others), By End User (Pharmaceutical and Biotechnology Companies, Healthcare IT, Diagnostic Companies, Clinical Research Organization, Research Institutes), By Region, Competition Forecast & Opportunities, 2026”, the global precision medicine market is expected to reach USD66.85 billion during the forecast period. The growth can be attributed to the growing geriatric population and rising research & development activities across different countries.
According to another TechSci research report on “Global AI in Drug Discovery Market By Component (Software v/s Services), By Technology (Machine Learning, Deep Learning, Others), By Drug Type (Small Molecule v/s Large Molecule), By Application (Target Identification, In Silico Drug Design, Drug Development, Big Data Analytics, Others), By Diseases (Immuno-oncology, Neurodegenerative Diseases, Cardiovascular Diseases, Metabolic Diseases, Others), By End User (Pharmaceutical & Biotechnology Companies, Contract Research Organizations, Research Centers and Academic & Government Institutes), By Region, Forecast & Opportunities, 2025”, the global AI in drug discovery market is anticipated to grow at a formidable rate during the forecast period. The growth can be attributed to the increasing R&D activities and software launches by major market players as well the growing need to shorten drug delivery process.
